-
Mon-Fri : 8am - 4pm
Sip Trunking
section-fbf7439
Metcom SIP Trunks
How SIP Trunks Work
SIP Trunking acts as a virtual connection between an organisation and an Internet Telephony Service Provider (ITSP) either via lines that link SIP trunks to other IP traffic, or through the Internet via a Virtual Private Network (VPN).
During a call, you can have any of the following scenarios and more:
- Be on a voice call with one other person
- Have multiple people on a conference call
- Run video calls
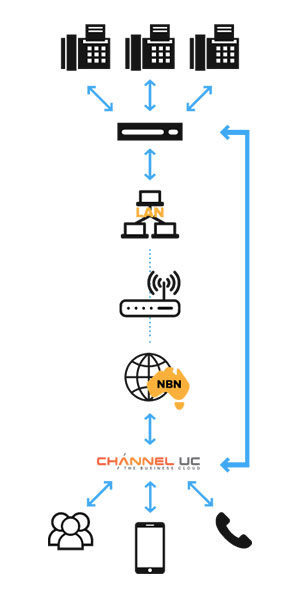
See the diagram on the right showing how calls flow from a SIP phone (VoIP) in a business to the internet. Nowadays, instead of routing voice calls over copper lines, SIP trunking sends them over data networks. In other words, the physical phone line is replaced with a virtual one which provide better quality voice solutions. The setup you’ll need to make the switch to SIP trunking includes the following:
- NBN Internet connection
- SIP-compatible PBX (Private Branch Exchange) box, also called IP PBX
- VoIP phone, or VoIP adapters if you’ll use your existing traditional phones
Metcom supply & install Epygi IP PBX systems and range of IP Phones & Telephony products to suit. Visit our shop or contact us for a quote.
section-8c84a97
IP PBX Systems
IP PBX & Deskphones
section-3b8983c
SIP Trunking
Pricing Plans
SIP Unlimited 4
- Unlimited Calls to Landline, Mobile, 13/1300
- 1 x DID Number
- 4 Lines/Channels
- Self Managed Portal
SIP Trunk Unlimited
- Unlimited Calls to Landline, Mobile, 13/1300
- 10 x DID Numbers
- Minimum of 4 Lines/Channels
- Multi System Compatibility
*T&C Apply. SIP Plans are subject to system compatibility and don't include PBX management unless the PBX was supplied and installed by Metcom
© Copyright Metcom 2021 All Rights Reserved Terms & Conditions










